- Published on


"I fought in our Revolutionary War for liberty."
—Sgt. John Vance
"...one of the most perfect battalions of the American Army."
—George Bancroft
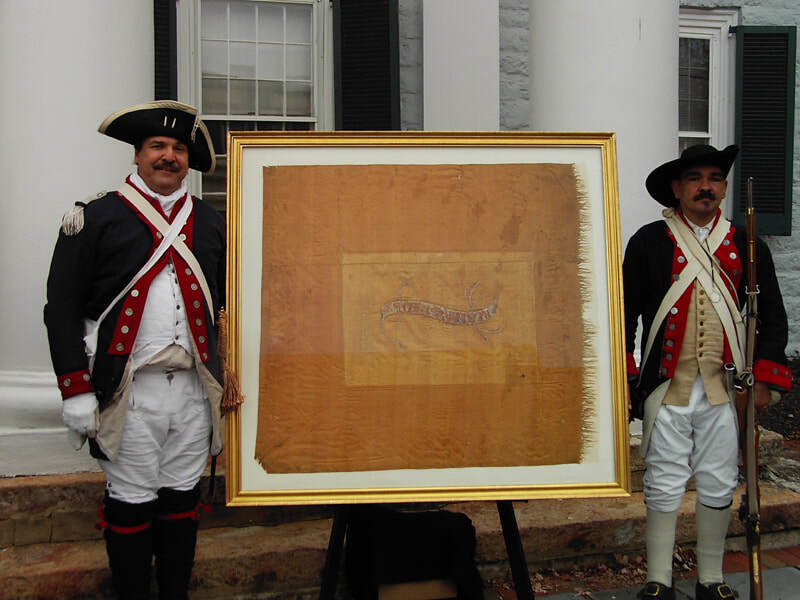

Rob Andrews and Erik Dorman guard an 8th Virginia division standard in front of the Shenandoah County Courthouse in Woodstock, Virginia in 2012. (Courtesy of Rob Andrews)
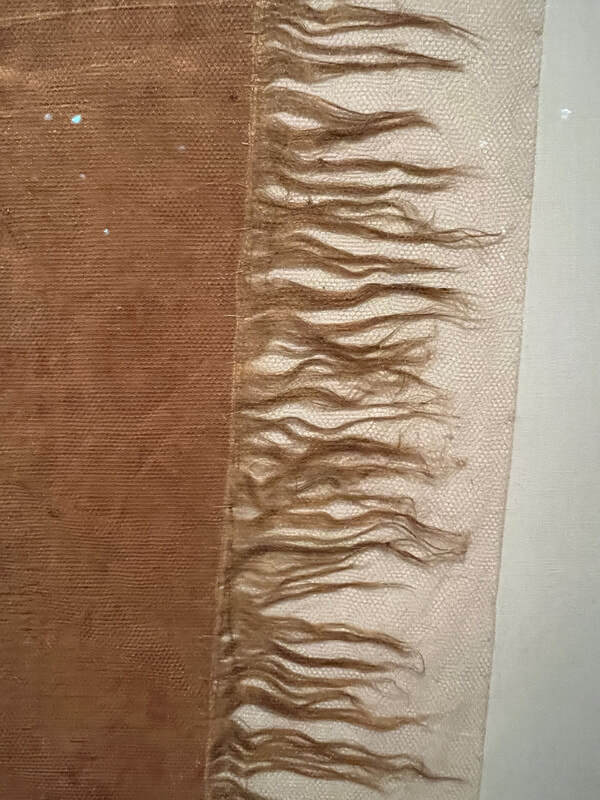

A close-up of the flag's fringe also shows the netting that is used conserve the flag. (Author)

The repainted side of the flag as displayed before 2012. Exposure to light resulted in a rectangle of faded fabric in the center of both sides of the flag. (Courtesy of R. Andrews)

The "3rd Virginia Detachment" banner captured by Banastre Tarlton in 1780.




The grand division standard as it likely appeared when new, recreated by 8th Virginia Regiment reenactor Nathan Gibson. (Courtesy of Nathan Gibson)

The first page of James Johnston's 1832 pension application affidavit, filed in Giles County, Va. (Fold3.com)

Johnston's name is included on a marker listing known Revolutionary War soldiers from Giles County. The plaque is located on the courthouse grounds in Pearisburg, Virginia. (HMDB.org
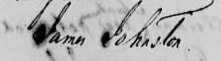


The lichen-encrusted grave of Abraham Bowman in Lexington, Kentucky. No portraits of Bowman or Helphenstine survive. Though Helphenstine is known to be buried in the Lutheran section of Winchester's Mount Hebron Cemetery, there's no surviving marker. It may be that his destitute widow was not able to afford a stone memorial. (author)

Peter Muhlenberg portrayed at the end of the war as a brevet Major General.






